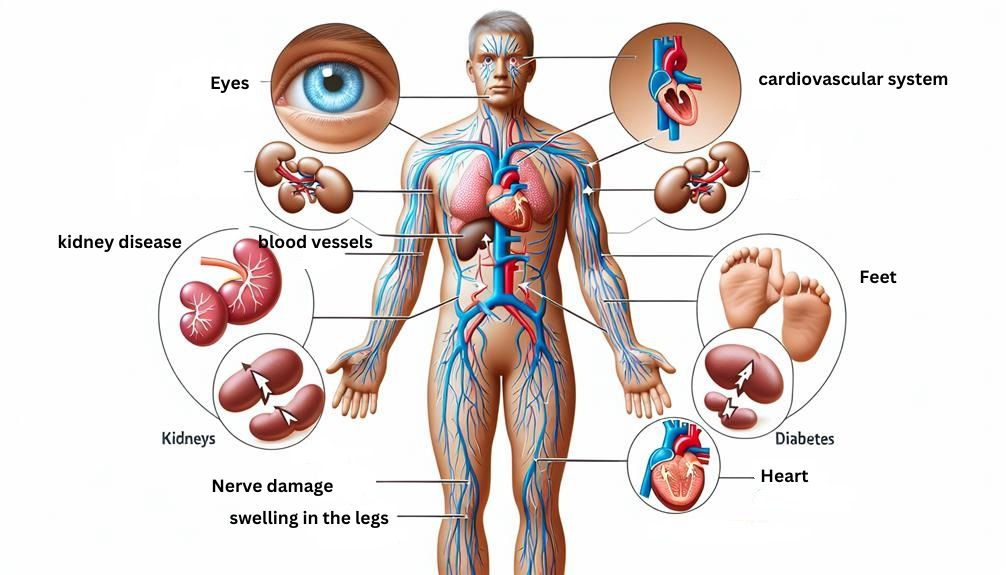
Diabetes impacts your body extensively and there are a whole range of effects of diabetes on the body you should understand. High blood sugar damages blood vessels, leading to heart problems. It affects kidney function, causing swelling and fatigue. Nerve damage from diabetes results in numbness. Eye health suffers due to retina damage, leading to blurred vision. Skin wounds heal slower, raising infection risks. Reproductive issues like fertility and erectile dysfunction may occur. Make sure to manage blood sugar effectively for better health. More detailed insights on the effects of diabetes await…
Key Takeaways of the Effects of Diabetes on the Body
- Diabetes damages blood vessels, affecting the cardiovascular system.
- High glucose levels harm kidneys, leading to diabetic nephropathy.
- Nerve damage from diabetes causes neuropathy and cognitive issues.
- Diabetic retinopathy impacts vision by damaging retina blood vessels.
- Uncontrolled diabetes disrupts skin health, delaying wound healing.
Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system in individuals with diabetes frequently exhibits heightened susceptibility to various complications, notably due to prolonged exposure to elevated blood sugar levels. High levels of glucose in the bloodstream can damage the blood vessels over time, leading to a condition known as atherosclerosis. In atherosclerosis, the blood vessels become narrowed and hardened, increasing the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
Moreover, diabetes can also affect the function of the heart muscle itself. With uncontrolled diabetes, the heart may experience changes in its structure and function, leading to conditions such as diabetic cardiomyopathy. This can result in symptoms like shortness of breath, swelling in the legs, and fatigue.
It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to closely monitor their blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and follow their healthcare provider's recommendations to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and medication adherence are key components in managing diabetes and protecting the cardiovascular system from further damage.
Kidneys and Urinary System
Excessive glucose levels in your system due to diabetes can lead to significant damage to your kidneys and urinary system over time. The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste from your blood, but when blood sugar levels are consistently high, the kidneys have to work harder, causing strain. This can result in diabetic nephropathy, where the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys become damaged, leading to decreased kidney function.
As diabetes progresses, the risk of developing diabetic kidney disease increases. Symptoms may include swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or hands, increased need to urinate, fatigue, nausea, and itchy skin. If left uncontrolled, diabetic kidney disease can progress to kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.

To prevent or slow down kidney damage, it's essential to manage your blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes. Regular monitoring of kidney function through blood tests is also crucial to detect any issues early on. By taking proactive steps, you can help protect your kidneys and urinary system from the damaging effects of diabetes.
Nervous System
High levels of glucose in your system due to diabetes can have detrimental effects on your nervous system, impacting its function and overall health. The nervous system is highly sensitive to changes in blood sugar levels. Prolonged periods of uncontrolled diabetes can lead to nerve damage, a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. This damage often starts in the extremities, such as the feet and hands, causing symptoms like numbness, tingling, or burning sensations. As the condition progresses, it can affect other parts of the body, leading to digestive issues, dizziness, and even problems with the heart.
Moreover, diabetes can also increase the risk of developing cognitive problems. Research has shown that individuals with diabetes have a higher likelihood of experiencing cognitive decline and an increased risk of conditions like Alzheimer's disease. It's crucial to manage your blood sugar levels effectively through medication, diet, and exercise to help prevent these complications and preserve the health of your nervous system.
Eyes and Vision
Elevated glucose levels in diabetes can significantly impact the health and function of your eyes and vision. The primary way diabetes affects the eyes is through diabetic retinopathy, a condition that damages the blood vessels in the retina. This damage can lead to vision problems and even blindness if left untreated. Additionally, diabetes increases the risk of developing other eye conditions such as glaucoma and cataracts.
Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can cause fluctuations in your vision, making it difficult to focus. You may experience blurred vision, double vision, or trouble seeing out of the corners of your eyes. Regular eye exams are essential for individuals with diabetes to monitor any changes in vision and detect eye conditions early.
Furthermore, diabetes can also affect the delicate nerves that control the eye muscles, leading to difficulties in eye movement and coordination. Proper management of blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes is crucial in preserving your eye health and vision.

Skin and Wound Healing
Diabetes impacts skin health and wound healing processes by disrupting the body's ability to efficiently repair and regenerate damaged tissues. When diabetes isn't well-managed, several complications can arise in skin and wound healing:
- Delayed Healing: High blood sugar levels can slow down the body's healing process, leading to longer recovery times for wounds and injuries.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Poorly controlled diabetes can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections in wounds.
- Nerve Damage: Diabetes can cause nerve damage, leading to a loss of sensation in the extremities. This lack of feeling can result in unnoticed injuries that may worsen due to impaired healing processes.
Effective management of blood sugar levels, proper wound care, and regular monitoring are essential to mitigate the impact of diabetes on skin health and wound healing.
Reproductive System
The impact of diabetes on the reproductive system manifests in various ways, affecting both male and female fertility and reproductive health. In males, diabetes can lead to erectile dysfunction (ED) due to damage to blood vessels and nerves. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the risk of ED. Additionally, diabetes can lower testosterone levels, impacting sperm production and quality.
In females, diabetes can disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods or even amenorrhea. Uncontrolled diabetes during pregnancy poses risks such as miscarriage, stillbirth, or birth defects. The condition also heightens the likelihood of gestational diabetes.
Diabetes-related complications like neuropathy can affect sexual response in both genders, diminishing libido and causing discomfort. Proper management of blood sugar levels, regular check-ups, and leading a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate these effects. Seeking medical advice for tailored treatment plans is crucial to safeguard reproductive health when living with diabetes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the effects of diabetes on the body are vast and impactful. From the cardiovascular system to the kidneys, nerves, eyes, skin, and reproductive system, diabetes can wreak havoc on multiple organs.
The juxtaposition of these physiological disruptions highlights the severity of the disease, evoking a sense of urgency for proper management and treatment. It's crucial to address diabetes with meticulous care to mitigate its detrimental effects on the body.




